Qihengxing's product - StarPure High-Resolution Agarose (FS-E1001) contributed spark power to this research with its excellent performance!
 Tumor vaccines that activate the immune system to eliminate tumor cells are a type of cancer immunotherapy. Effective method. Traditional cancer vaccines are divided into two categories: tumor-associated antigen vaccines and personalized neoantigen vaccines. Although these traditional cancer vaccines have achieved remarkable results in clinical trials in recent years, they still face challenges such as tumor heterogeneity, limited antigen selection, insufficient antigen presentation, and slow immune response, resulting in poor universality and response rates. In contrast, pathogen-specific immunity acquired through infection or vaccination can rapidly generate more effective and long-lasting immune responses upon re-encountering the same antigen. The receptor binding domain (RBD) of SARS-CoV-2 is highly immunogenic, and global COVID-19 vaccination has enabled a large number of people to develop pre-existing RBD-specific immunity. Recently, a paper published in Advanced Materials, titled "A Universal Therapeutic Vaccine Leveraging Autologous Pre-Existing Immunity to Eliminate in Situ Uniformly Engineered Heterogeneous Tumor Cells," describes a novel universal therapeutic tumor vaccine. This vaccine utilizes an adeno-associated virus (AAV) vector to genetically engineer a variety of tumor cells to overexpress and efficiently present the highly immunogenic SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain (RBD). This vaccine then awakens and enhances pre-existing immune responses against the RBD, thereby achieving in situ clearance of multiple tumor cells (Figure 1). The results of the study showed that this vaccine can significantly inhibit tumor growth, induce antigen spread, and stimulate a broad range of tumor-specific cellular immune responses, providing new ideas for overcoming tumor heterogeneity and the limitations of personalized medicine. The researchers selected AAV as a vector, leveraging its high safety, broad tissue tropism, and sustained transgene expression capacity to design a vaccine that enables tumor cells to overexpress and efficiently present RBD. Through structural optimization, they engineered a gene sequence capable of simultaneously expressing trimeric RBD on the cell membrane and releasing RBD-encapsulated virus-like particles (eVLPs) to awaken and enhance RBD-specific immunity. Short-shRNAs that silence PD-L1 and SUSD6 were embedded within the AAV vector to enhance cytotoxic T cell-mediated tumor killing. Furthermore, AAV and the CpG1018 adjuvant were encapsulated in a thermosensitive hydrogel for localized delivery, ensuring sustained antigen expression and immune activation while minimizing systemic side effects.
Tumor vaccines that activate the immune system to eliminate tumor cells are a type of cancer immunotherapy. Effective method. Traditional cancer vaccines are divided into two categories: tumor-associated antigen vaccines and personalized neoantigen vaccines. Although these traditional cancer vaccines have achieved remarkable results in clinical trials in recent years, they still face challenges such as tumor heterogeneity, limited antigen selection, insufficient antigen presentation, and slow immune response, resulting in poor universality and response rates. In contrast, pathogen-specific immunity acquired through infection or vaccination can rapidly generate more effective and long-lasting immune responses upon re-encountering the same antigen. The receptor binding domain (RBD) of SARS-CoV-2 is highly immunogenic, and global COVID-19 vaccination has enabled a large number of people to develop pre-existing RBD-specific immunity. Recently, a paper published in Advanced Materials, titled "A Universal Therapeutic Vaccine Leveraging Autologous Pre-Existing Immunity to Eliminate in Situ Uniformly Engineered Heterogeneous Tumor Cells," describes a novel universal therapeutic tumor vaccine. This vaccine utilizes an adeno-associated virus (AAV) vector to genetically engineer a variety of tumor cells to overexpress and efficiently present the highly immunogenic SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain (RBD). This vaccine then awakens and enhances pre-existing immune responses against the RBD, thereby achieving in situ clearance of multiple tumor cells (Figure 1). The results of the study showed that this vaccine can significantly inhibit tumor growth, induce antigen spread, and stimulate a broad range of tumor-specific cellular immune responses, providing new ideas for overcoming tumor heterogeneity and the limitations of personalized medicine. The researchers selected AAV as a vector, leveraging its high safety, broad tissue tropism, and sustained transgene expression capacity to design a vaccine that enables tumor cells to overexpress and efficiently present RBD. Through structural optimization, they engineered a gene sequence capable of simultaneously expressing trimeric RBD on the cell membrane and releasing RBD-encapsulated virus-like particles (eVLPs) to awaken and enhance RBD-specific immunity. Short-shRNAs that silence PD-L1 and SUSD6 were embedded within the AAV vector to enhance cytotoxic T cell-mediated tumor killing. Furthermore, AAV and the CpG1018 adjuvant were encapsulated in a thermosensitive hydrogel for localized delivery, ensuring sustained antigen expression and immune activation while minimizing systemic side effects.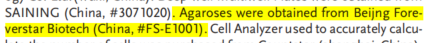
Qihengxing's product - StarPure High-Resolution Agarose (FS-E1001) contributed spark power to this research with its excellent performance!
AAV-DJ achieved an infection efficiency exceeding 99% in B16F10, 4T1, and CT26 tumor cells. The STMHR sequence successfully achieved transmembrane and secretory expression, while shRNA effectively silenced the PD-L1 and SUSD6 genes. In mice pre-vaccinated with an inactivated vaccine or mRNA vaccine, treatment with this vaccine significantly increased RBD-specific antibody titers and enhanced cellular immune responses. In multiple tumor models, the vaccine significantly inhibited tumor growth and prolonged survival, with some mice even achieving complete remission. The treatment process induced antigen diffusion and stimulated immune memory against RBD and the original tumor cells. In addition, the vaccine showed good therapeutic effects in mouse models with different HLA genes, indicating its potential universality.
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of a universal therapeutic vaccine that utilizes autoimmunity to eliminate multiple in situ tumor cells. In summary, the AAV-based universal therapeutic vaccine developed in this study can efficiently and specifically eliminate genetically modified tumor cells by awakening and enhancing pre-existing immune responses. The vaccine enhances anti-tumor immune responses by improving antigen presentation, increasing membrane antigen expression, and inducing antigen diffusion. It has demonstrated promising anti-tumor efficacy and safety in multiple tumor models, potentially breaking through HLA restriction and providing a new universal strategy for cancer immunotherapy.
 Tumor vaccines that activate the immune system to eliminate tumor cells are a type of cancer immunotherapy. Effective method.
Tumor vaccines that activate the immune system to eliminate tumor cells are a type of cancer immunotherapy. Effective method.